Weston Middle School
Technology/EngineeringCourse Materials
| Powerful
Idea |
Description |
|
| What is a Robot? | A robot is an autonomous system which:
|
|
| Prototypes | A prototype is a working test model of a machine that solves some problem. The Lego NxT system is a prototyping system as it permits rapid construction and modification of designs. |
|
| Engineering Design | Engineering design is a cycle of being given a problem, researching possible design solutions, building, testing, and modification/improvement. An elegant design is the simplest design which effectively performs the desired task. |
|
| Computer
Programming |
This is the fundamental idea that robots are not living things that act of their own accord. Instead, robots act out computer programs written by human beings. Programs are
written by carefully describing the desired behavior of the robots
(algorithm), then translating this into a computer language ( such
as NxT-G). |
|
| Machine Hardware | The physical structure of a robot includes :
|
|
 |
||
| Gears and Mechanisms | Gear trains can be used to gain mechanical advantage in speed (gearing up) or torque( gearing down), and change the direction or axis of rotation. Mechanisms convert linear motion into rotation and vice versa. |
|
 |
||
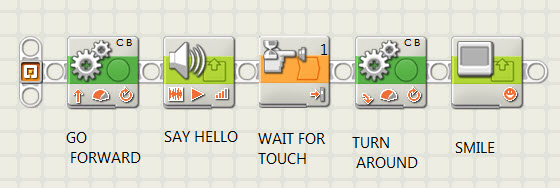
| Command
Sequences & |
The idea that simple commands can be combined into sequences of actions to be acted out by a robot in a linear sequence or in parallel sequences. |
|
 |
||
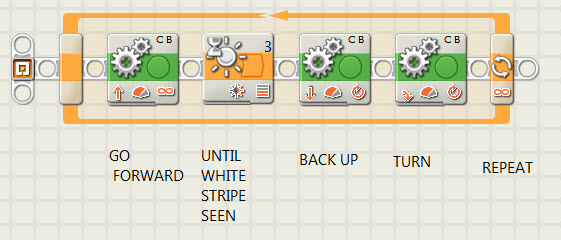
| Loops |
The idea that sequences of instructions can be modified to repeat indefinitely or in a controlled way ( such as loop until touched or for a certain time). |
|
|
||
| Sensors ( 'wait
fors') |
The idea that a robot can sense its surrounding environment through various sensors, and that a robot can be programmed to respond to changes in its environment. |
|
 |
||
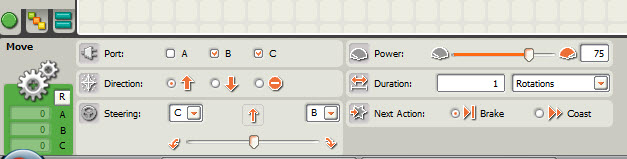
| Parameters |
The idea that some instructions can be qualified with additional information. |
|
 |
||
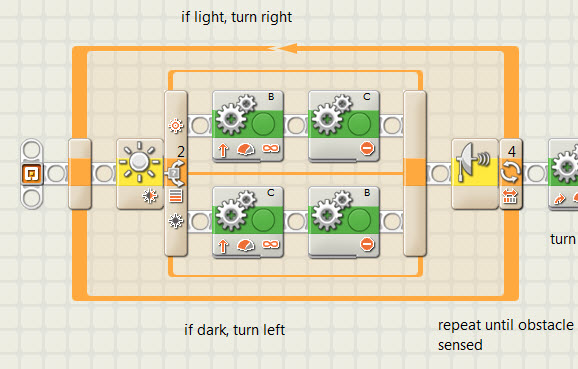
| Conditional
branches (switches) |
The idea that you can ask a question in a program, and, depending on the answer, have a robot do one thing or another. | |
 |
||
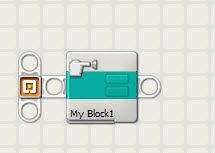
| Subroutines ( My
Blocks) |
The idea that you can treat a set of instructions as a single unit that can be called from other parts of a program. | |
 |
||
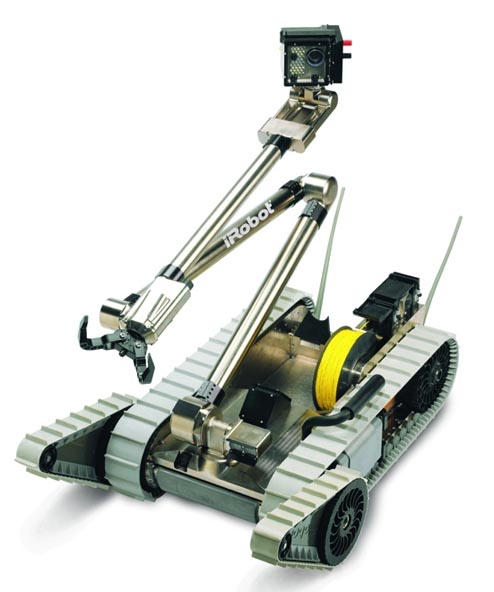
| Robot Applications | Robots have traditionally been used to perform tasks which are dirty, dull(repetitive), or dangerous. Examples of such robots include:
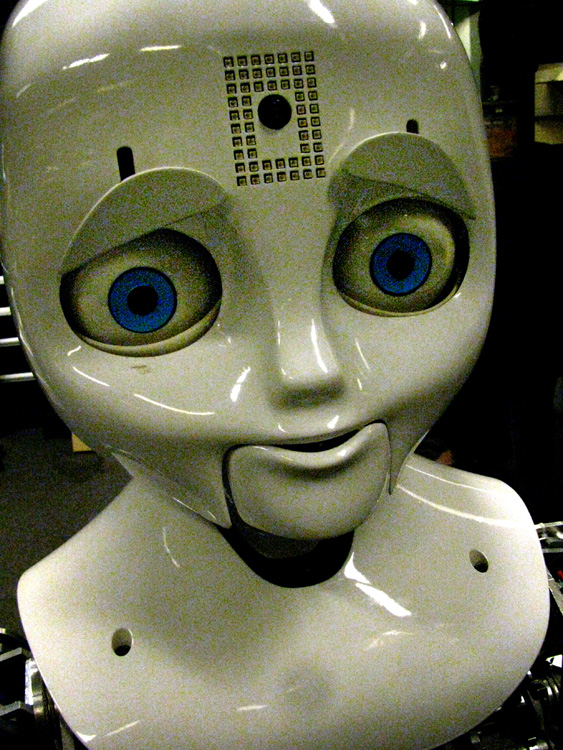
Robots are also used to augment or replace human functions, such as: |
|
| Based on: Storytellers and engineers in early childhood: developing technological fluency by making robots by Marina
U. Bers DevTech
Research Group |
||
 Sociable
Robots Sociable
Robots |
||
IRobot Packbot
|
||
Links
EditRegio
Yoky Matsuoka with prosthetic arm